Question:
This assessment tests the learning outcomes and module content of:
Module: Driving Value through Procurement and Supply
Module: Managing Expenditures with Suppliers
Task
Identify a product, service or category of spend and outline its importance and impact to your organisation’s stakeholders. Prepare a brief market analysis and demonstrate how your procurement function will produce
value for money outcomes. Your final submission should also review the current approaches to managing prices and costs for the product, service or category you have identified, as well as highlighting the impact of
markets to secure cost savings for your organisation.
SOLUTION/ANSWER
Table of Contents
1.1 Background of the ADNOC Refining. 4
1.2 Procurement Division in ADNOC Background. 4
2.0 ADNOC Stakeholders Analysis 5
3.1 Relevance of Stakeholders in the Identified Area of Spend. 7
3.2 Stakeholders Impact on Procurement from ADNOC Context 8
4.0 Research and Market Analysis 9
4.1 Procurement of Nanotechnology fitted Pipes Analysis 9
5.2 Applicable Variables in Nanotechnology Fitted Pipes Procurement 11
5.4 Industrial Competitiveness 12
6.0 Current Strategies and Approaches 13
8.0 Nanotechnology fitted Pipes Market Analysis Techniques 15
8.4 Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis 18
9.0 Conclusion and Recommendations 19
Appendix 1: Workflow of procurement in the ADNOC. 23
Appendix 2: Supplier group registration form.. 24
Appendix 3: ADNOC Organisational Structure. 26
Appendix 4: Organisation Structure in ADNOC. 27
Executive Summary
In this first assessment, it analyses and evaluates the Abu Dhabi Company (ADNOC) procurement strategies to gain value for money and quality. To achieve this, the selected area of spend is modern pipes with nanotechnology as an added advantage. As a senior procurement specialist in ADNOC Gas processing, the author is interested in overseeing the procurement of this area of spend. Also, by being involved in the departments of contracting, purchase, commercial directory, strategic sourcing, and the operations of the entire procurement department, the relevant information is obtained. Through engagement on different stakeholders, they have been identified to play a critical role in ensuring an improved procurement process.
In the analysis, this report has followed a detailed analysis of data in the category of spend, marketing analysis, and market positioning. Different tools have been applied in this analysis, which includes the PESTEL, Kraljic, SWOT, Porters 5 forces, and Ansoff Matrix analysis. Based on the obtained findings of this study, it is evident that the ADNOC refining company sourcing of the nanotechnology pipes, it is yet to gain a lot of popularity in terms of a limited number of suppliers interested.
From the report findings, several recommendations are suggested which are the desire for improvement of the value addition by improving their positioning. Also, they must strengthen their relationship with the existing stakeholders. Also, they must integrate into their policies the need for active resource management since the pipes fitted with nanotechnology require value for money as opposed to the standard pipes. This has been identified in this report as the need to integrate an appropriate procurement planning.
1.0 Introduction
1.1 Background of the ADNOC Gas Processing
ADNOC gas processing has existed for more than 46 years, where it is actively involved in Abu Dhabi’s development economically as a leading oil producer locally and globally (ADNOC, 2020). ADNOC leverages modern innovativeness to maximise the value of their resources. Through this and ensuring they receive the value for money in their engagement with different stakeholders, they ensure they are appropriately positioned in their market. This is meeting the consistent changing demands of their energy market, which positively impacts their economy and future operations.
1.2 Procurement Division in ADNOC Background
ADNOC Gas processing organisation operates an independent procurement division tasked with the function to harness competitiveness and sustainability of their supply chain by engaging different stakeholders. As a strategy of embracing technology and to have a value for their money, ADNOC operates a technology-based registration system that is prompt (see appendix 2). It is a requirement for all organisation suppliers to fill unrepeated login to the ADNOC commercial recording where they qualify to do business in all sectors of gas processing (see appendix 1). Through this, the organisation has managed to put in place procurement strategies collaboratively among all the departments since they present their procurement needs independently for successful tending and bidding strategies. Further, procurement division operations and supply division are implemented strictly through adhering to terms, conditions and legislations. These include pricing, risk management, and strict adherence to the organisation supply timelines.
There are different characteristics of the ADNOC gas processing procurement department that makes it to be unique (see summary in figure 1).
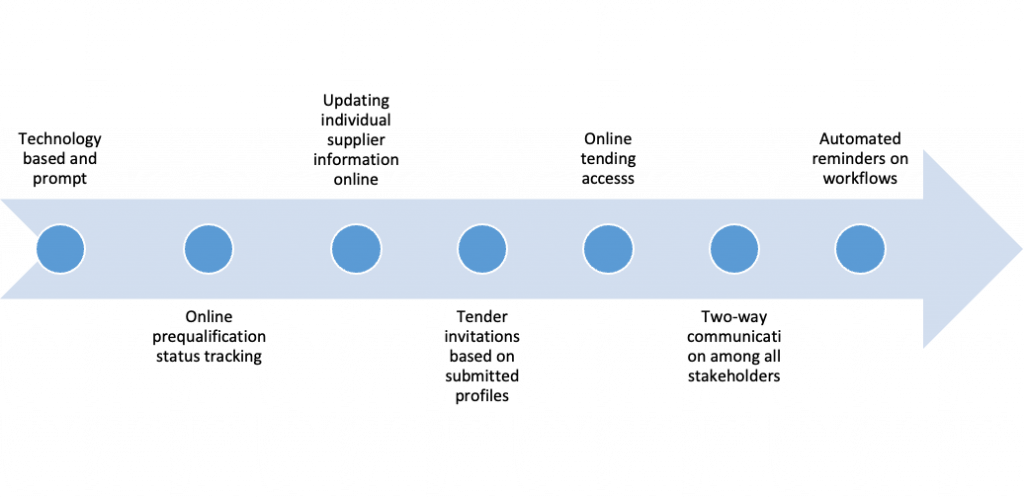
Figure 1: Features of the ADNOC procurement Division activities
1.3 Scope of Assessment
Since ADNOC has a broad range of procurement and supply in its onshore and offshore operations, this report is narrowed to focus on pipes fitted with nanotechnology as the category of spend. Through the use of the pipes as a spend area, this report analyse and evaluates the scope in which the ADNOC stakeholders implement sustainable procurement practices. This is by assessing how their operations lead to cost-saving and value addition in their operations. Additionally, the availability of the suppliers, the need for the embrace of technology in the procurement process, services provision to their customers, and the best approaches in gaining value for invested resources with an evaluation provided.
2.0 ADNOC Gas Processing Stakeholders Analysis
In CIPS, the stakeholders are identified as a group of individuals, eliciting a direct influence on the strategies, goals, and organisation policies (CIPS, 2017). In a general context, stakeholders can include creditors, directors, employees, governments, stakeholders, and customers. Stakeholders are nevertheless varying from one organisation to the other and significantly influenced by their operations in their market. They are nonetheless categorised to;
- Internal
- Connected
- External stakeholders (CIPS, 2010)
Taking into account of ADNOC Gas Processing company, their internal stakeholders can be grouped into partners, staff and the administration which include the PS&M department, contracting, sourcing and even the IT tasked with commercial directory. The internal stakeholders also include their different subsidiaries (ADCO, ADMA-OPCO, ZADOC, Al Yasat, Al Dhafra, and NDC).
The external stakeholders are the communities, legislation institutions, NGOs (such as environmental groups) and organisations they are competing. The competitors include Shell, Total, BP, JODCO, and Exxon-Mobil.
For the connected stakeholders, on the other hand, involve the government institutions owing to the 80% of UAE government ownership of ADNOC, customers, and supplies.
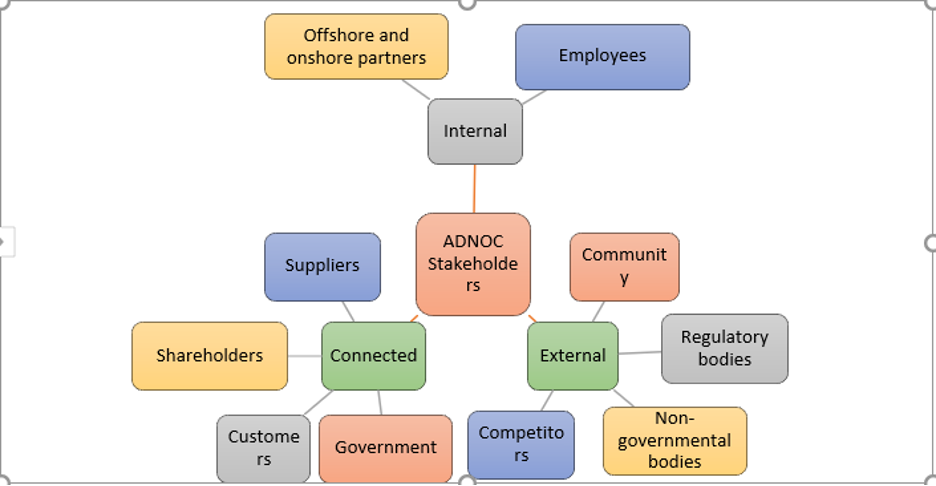
Figure 2: Categories of ADNOC Stakeholders
Further, by using a stakeholder’s management matrix CIPD (2019), it is possible to analyse the positioning of the identified stakeholders (see figure 3);
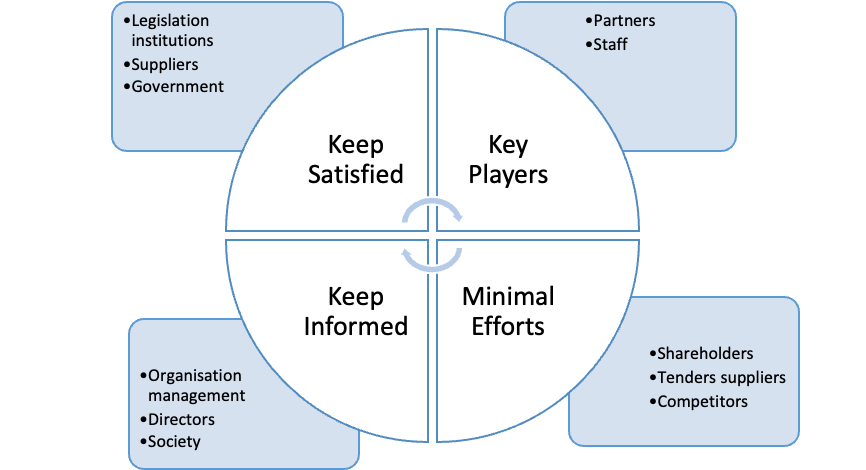
Figure 3: ADNOC Gas processing stakeholders analysis matrix
Keep Satisfied:
This group that need to be satisfied include the suppliers, the regulators and government. They have a major influence on the organisation value for money and quality received from the procurement process.
Key Players:
Partners and staff are supposed to be aware of any potential change process, being updated with any form of medication demanded and awareness of their relevance.
Keep informed:
This group include the management, different directs and society who play a critical role in the procurement plan status, any issues or challenges, and further requirements, occurring of unplanned activities as well as any risks, might be in place.
Minimal Efforts:
Shareholders and competitors are supposed to operate through an active monitoring in regard to the available plans. Through the plans monitoring process, any likely risk is mitigated.
3.1 Relevance of Stakeholders in the Identified Area of Spend
In the ADNOC procurement division, there are always contracts that are being implemented in sourcing the pipes fitted or not fitted with nanotechnology for their different distribution activities. The contracts are executed for the engineering, offshore and onshore facilities, drilling, and manufacturing departments. The pipes are used in the ADNOC company processing, drilling process, and wells maintenance. Also, the pipes are used in extracting crude oil from their different reservoirs. Since the identified stakeholders take part in either construction, operations, facilities management, processing, and quality assurance, they play a critical role in procurement of nanotechnology fitted pipes is enhanced. These pipes are essential for ADNOC business and partnership, which is advanced by the different identified stakeholders. Also, the various stakeholders from different levels are hard to be satisfied. For attaining the most appropriate procurement process and gain value for money from competition, appropriate consolidation of plans and inclusion of all identified stakeholders ought to be evident.
3.2 Stakeholders Impact on Procurement from ADNOC Context
As part of the procurement division, there is a sub-division that is tasked with quality assurance of the pipes procured from different suppliers in the overall organisation. This has a positive impact on guiding ADNOC in achieving its set strategies. The piping department, as identified in ADNOC (2020), plays a critical role in making sure all operations are actively coordinated with all the other departments in the organisation. In particular, the new pipes which are fitted with nanotechnology offer the organisation with opportunities to leveraging on a competitive advantage. Due to the criticality of the nanotechnology fitted pipes procurement criticality to all the departments, it is relevant to increase the budgetary allocation in their procurement. Also, technology must be adopted as part of improved planning to ensure that they obtain accurate and timely data about all their practices in the overall value chain. Ultimately, there are improvements in the practices in both onshore and offshore, improved efficiency in procurement, and unlocking value for their money in the overall organisation initiatives.
Also, since increasing the budgetary allocation on the procurement of pipes fitted with nanotechnology would lead to a positive impact on the ADNOC ability to increase their agility, efficiency, and responsiveness, they would positively impact all the stakeholders. This is part of the ADNOC long-term strategy that intends to ensure that they practice innovativeness in maximising the value of the resources that they have. Apart from this, they have invested in technology to ensure that their organisations are positioned appropriately to attain the consistently changing energy market. This impacts the Abu Dhabi economy positively as part of its long-term strategy.
4.0 Research and Market Analysis
4.1 Procurement of Nanotechnology fitted Pipes Analysis
In 2019, ADNOC completed the $4 billion partnership for pipes procurement with BlackRock and KKR companies (National, 2019). This partnership would improve the organisation operations in the overall Middle-East energy sector, which is also supposed to obtain finances through adhering to capital markets traditionally in existence. For instance, in 2018, their overall spend on nanotechnology was approximately 17 million AED, which was further increased to 30 million AED in 2019. The spend categories included the procurement of materials, transport, fixing gas supplies, generating power, oil, and gas supply targeting end-users and subsidiaries. This is as illustrated in table 1;
| Procurement of Pipes fitted with nanotechnology | Year 2018 (M AED) | Year 2019 (M AED) |
| Material supplies | 5.3 | 3.5 |
| Transport costs | 7.7 | 9.3 |
| Gas pipes fixing | 0.15 | 6.7 |
| Generating power sources | 0.4 | 3.7 |
| Oil and gas supply from both onshore and offshore | 0.9 | 1.32 |
| Delivering to end-users to end-users and subsidiaries | 2.4 | 5.5 |
| Total | 17.03 | 30.02 |
Table 1: Nanotechnology fitted pipes procurement (2018 & 2019)
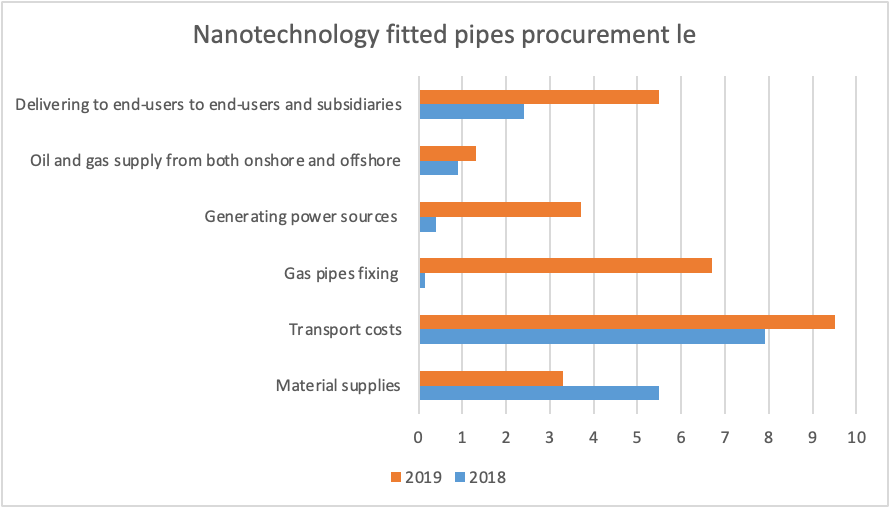
Figure 4: Nanotechnology fitted pipes procurement (2018/2019)
As illustrated in figure 4 and table 1, there has been a significant increase in the amount spent in procurement of the nanotechnology pipes in 2019 which is contrary to the spending in year 2018. The rationale of this can be identified as the latest ratification of the ADNOC organisation to harness both their onshore and offshore practices. This can equally be enhanced by the recent agreement with the BlackRock and KKR organisations to support their access to nanotechnology pipelines. Also, the expansion of ADNOC to a new petrochemical value chain provides an appropriate investment in identified area of spend which is nanotechnology pipes holistically. This is in their storage areas, refinement, and distribution at the end (Gulf, 2016).
5.0 Market Analysis
5.1 Market Overview………………………………………………………………………………
Email address: rankedtutorials@gmail.com
